Error estimate of simulation of human artery under fibre activation
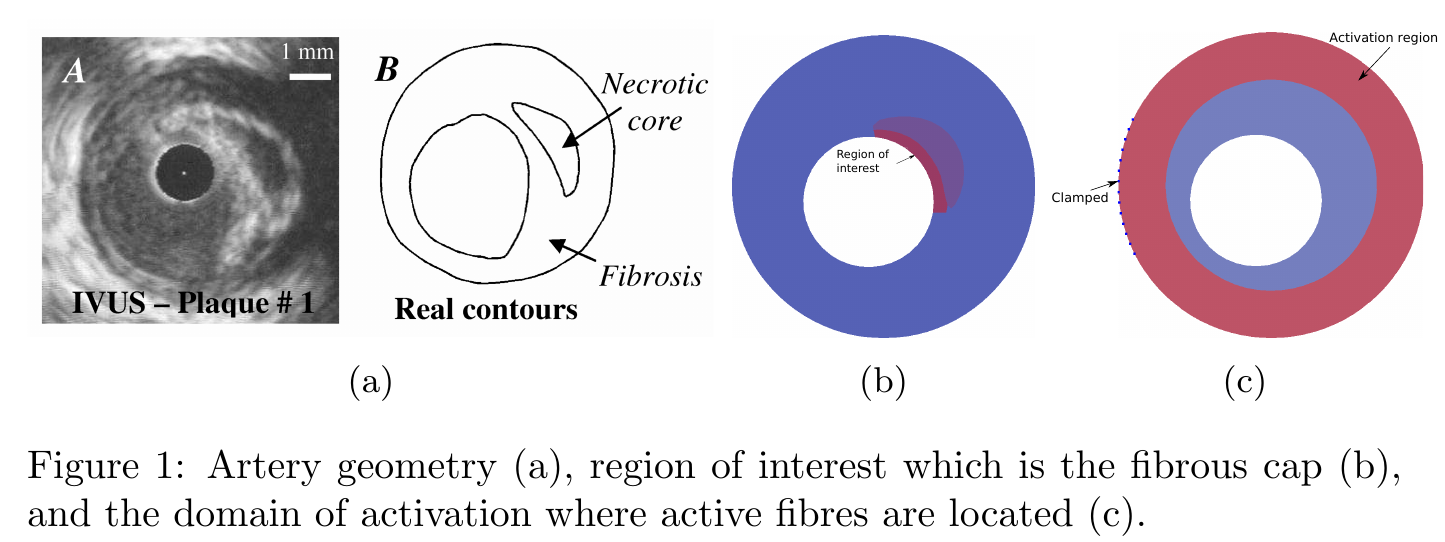
We study the behaviour of an human artery with a vulnerable atherosclerotic coronary plaque subjected to internal contractility. Artery geometry, boundary conditions, region of interest and the domain of activation where the active fibres are located are shown in Figure 1.
A Saint Venant-Kirchhoff material is employed to model the behaviour of the artery. We consider that the strain within the fibrous cap is a good biomechanical predictor for the plaque rupture. We then define our quantity of interest during simulation as expressed by
with u the displacement solution, E the Green-Lagrange strain tensor and ω the domain of interest.
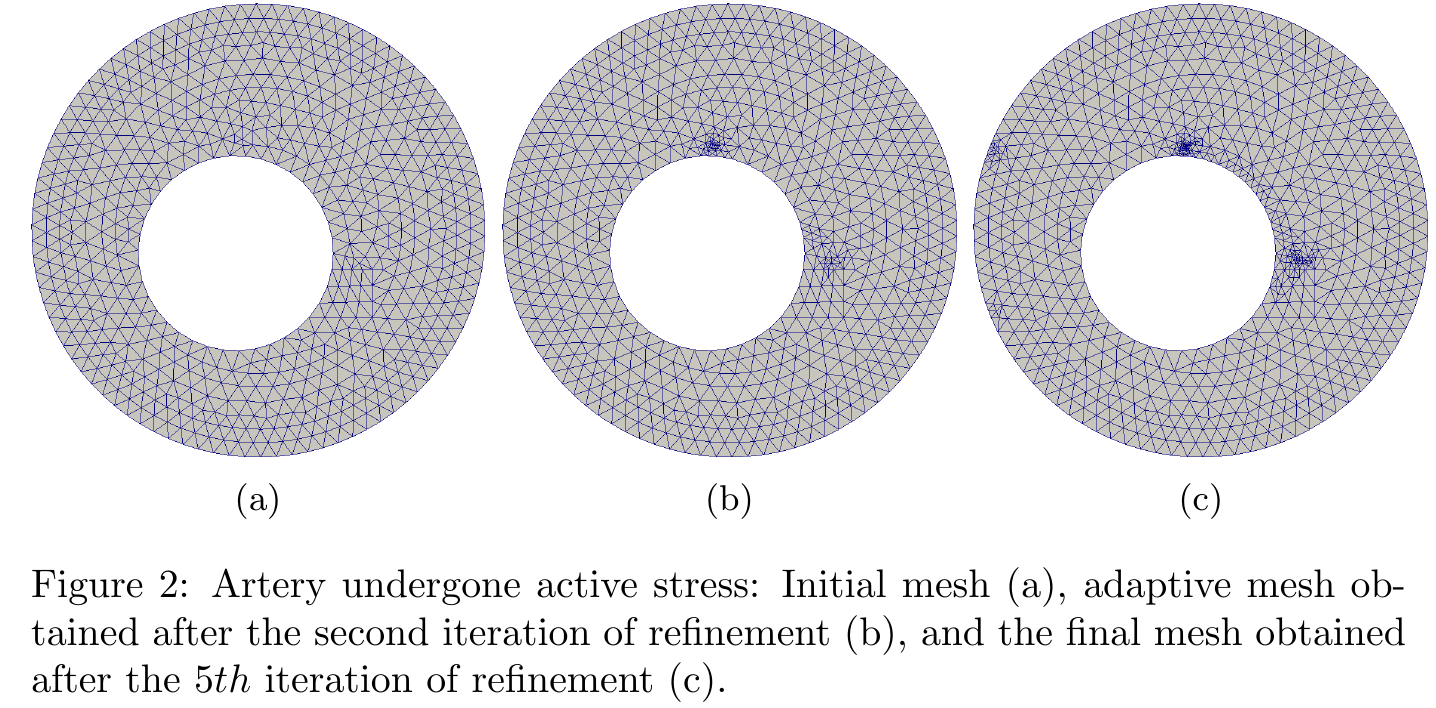
Using error estimates based on Dual weighted residual (DWR) method, we are able to estimate the error of the quantity of interest computed on the region of interest, and then adapt the mesh used for the simulation in order to reduce the error of the quantity of interest. Different mesh refinements are shown in Figure 2.